 When it comes to pneumatic conveying systems, there is a variety of "shop talk" used when researching and discussing this technology. While some terms are familiar or require just a little common sense to gain an understanding, there are also some lesser known terms and synonyms that are part of this specialized solids handling lingo - some you might not know at all unless you've worked with a pneumatic conveying system or manufacturer before. If you are less than familiar with this terminology, it can make it difficult to understand important data.
When it comes to pneumatic conveying systems, there is a variety of "shop talk" used when researching and discussing this technology. While some terms are familiar or require just a little common sense to gain an understanding, there are also some lesser known terms and synonyms that are part of this specialized solids handling lingo - some you might not know at all unless you've worked with a pneumatic conveying system or manufacturer before. If you are less than familiar with this terminology, it can make it difficult to understand important data.
We've put together a handy list of terms for you to reference as you are researching pneumatic conveying technology options. Most of the terms here will refer to various components used in a system and also specific characteristics that may determine what type of system it is. You will find that a lot of the terms listed below can be observed in certain safety standards like NFPA 654 or technical articles like you might find in various publications.
Air-Material Separator: A device designed to separate the conveying air from the material being conveyed.
Synonyms: Cyclone, Filter Receiver
Air-Moving Device: A power-driven device that establishes an airflow by moving a given volume of air per unit time.
Synonyms: Blower, Compressor, Vacuum Pump
Air Permeability: This is a measure of the ease with which air will pass through a bed of bulk particulate material when a pressure difference is applied.
Air Retention: The ability of a bulk material to retain air in the interstitial spaces between particles for a period of time.
Air-to-Cloth Ratio: The velocity per unit area at which a filter media is designed to withstand without creating excess pressure drop or causing premature wear/damage to the filter membrane.
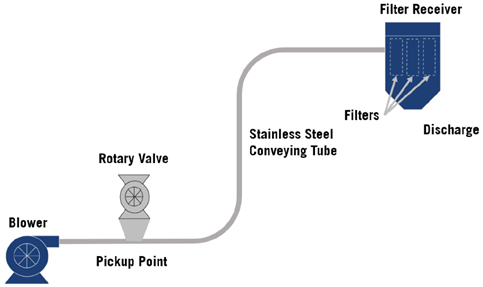
Dense Phase Conveying: The mode of pneumatic conveying which operates at higher solids/gas ratios. This type of flow is often observed by slugs or dunes of product moving through a pipeline. Solids/gas ratios are normally 15-20 or higher.
Dense Phase Conveyors: Typical Configuration
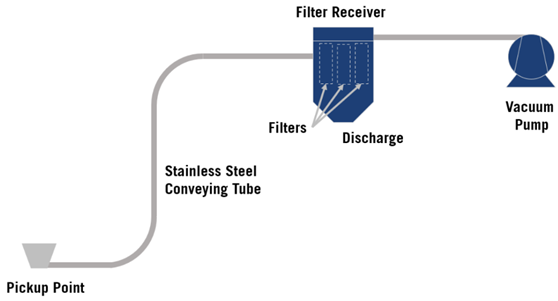
Dilute Phase Conveying: The mode of pneumatic conveying which operates at lower solids/gas ratios. This type of flow is often observed by a fully suspended product moving through a pipeline. Solids/Gas ratios are normally 10 or less.
Dilute Phase Conveyors: Typical Configuration
Duct: Enclosure used to convey materials pneumatically or by gravity.
Synonyms: Pipe, Tube
Dryer: A piece of processing equipment used to reduce the moisture content of the material being handled.
Pickup Adaptor: The entry point in a transfer line designed for mating with some type of storage/hopper vessel. Enables the ability to control the solid/gas loading ratio through a pipeline.
Synonyms: Pickup shoe, Pickup manifold
Rotary Valve: A metering device designed to control the flow of material into and out of a conveying system without affecting the system's differential pressure.
Saltation Velocity: The velocity at which material transitions from dense phase flow to dilute phase flow in a pipeline. In other words, the point at which the velocity goes high enough to suspend to particles within the pipeline instead of in slugs or dunes.
Solids/Gas Ratio or Solids Loading Ratio: The ratio of the mass flow rate of solids being conveyed to the mass flow rate of gas being used for conveying.
Suction Wand: A device designed for an operator to use at the beginning of a transfer line. It connects to the hose/duct inlet and is used to transfer material from open top containers. They often incorporate liner/bag guards and air intake control.
Synonyms: Suction lance
With this pneumatic conveying glossary in your arsenal, you'll be prepared for a discussion on pneumatic conveying that you can not only comprehend but be an active participate in. And if you still have questions? Well, that's what we're here for! Contact us and we'd be happy to discuss your powder handling needs.

